Hydrocarbon-Soluble Calcium Hydride
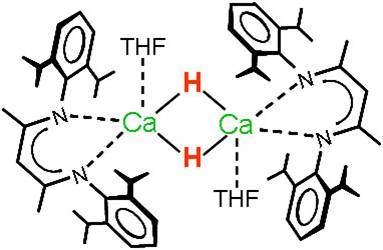
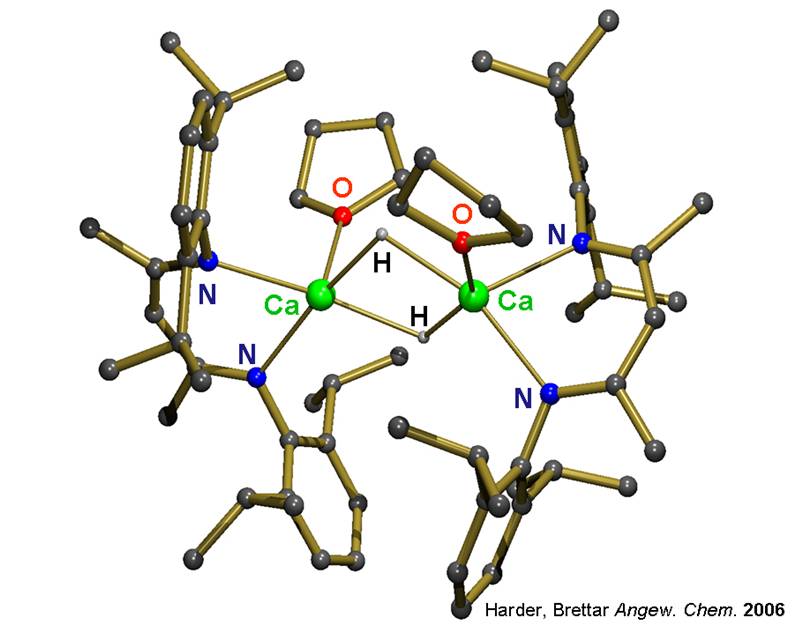
Although the early main group metal hydrides (LiH, NaH, CaH2) are well-established reagents, hardly any well-defined molecular hydride complexes are known. This is partly due to the lack of synthetic procedures but also related to their dynamic behaviour and the very high lattice energies of the salts (MH)∞ and (MH2)∞.
Attempted syntheses of calcium hydride complexes nearly always resulted in precipitation of CaH2. Use of N, N-chelating „nacnac“ ligands, however, enabled isolation of the first well-defined hydrocarbon-soluble calcium hydride complex. This initiated a rich reaction chemistry with the Ca-H functionality in organic solution.
(Harder, Brettar Angew. Chem. 2006)
The concept has been applied to several other small „inorganic“ anions like OH– and CN– and allows for typical inorganic reactivity in organic solvents.